Table Of Content

An experimental design where treatments aren’t randomly assigned is called a quasi-experimental design. You can either use full factorial designs with all possible factor combinations, or fractional factorial designs using smaller subsets of the combinations. The use of a control group is an important experimental design method that involves having a group of participants that do not receive the treatment or intervention being studied. The control group is used as a baseline to compare the effects of the treatment group.
Synthace combines ChatGPT and digital experiments in first step toward a true AI scientist - Business Wire
Synthace combines ChatGPT and digital experiments in first step toward a true AI scientist.
Posted: Wed, 24 May 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Planning and Organizing Designed Experiments
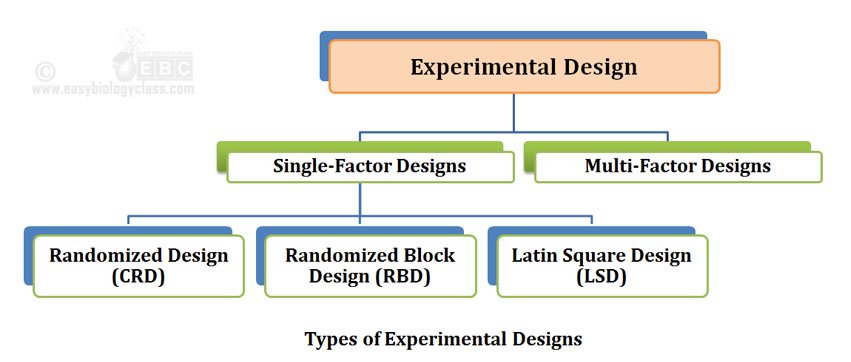
Main concerns in experimental design include the establishment of validity, reliability, and replicability. For example, these concerns can be partially addressed by carefully choosing the independent variable, reducing the risk of measurement error, and ensuring that the documentation of the method is sufficiently detailed. Related concerns include achieving appropriate levels of statistical power and sensitivity. Of all the types, the simplest type of experimental design is the completely randomized design, in which the participants are randomly assigned to the treatment groups. The main advantage of using this method is that it avoids bias and controls the role of chance.
Step 3: Design your experimental treatments
There are several types of regression analysis, including linear regression, logistic regression, and multiple regression. When conducting an experiment that tests only one factor, the impact of factors upon each other is missed. Design of experiment enables the project manager to learn about what happens when factors interact, thus providing a more accurate evaluation of quality. Project managers can use the data from a well-designed experiment in their Quality planning.
Step 1: Define your variables
A unique application of DOE in marketing is called conjoint analysis. A web-based company wanted to design its website to increase traffic and online sales. Doing a traditional DOE was not practical, so leadership decided to use conjoint analysis to help them design the optimal web page. Doing a designed experiment as opposed to using a trial-and-error approach has a number of benefits. You can visualize, explore your model and find the most desirable settings for your factors using the JMP Prediction Profiler.
Design of Experiments for Project Managers
Unfortunately, most process outcomes are a function of interactions rather than pure main effects. You will need to understand the implications of that when operating your processes. When discussing the proper settings for your process variables, people often rely on what they have always done, on what Old Joe taught them years ago, or even where they feel the best setting should be.
Applications of Experimental Design
However, the focus of the course is on the design and not on the analysis. Please include what you were doing when this page came up and the Cloudflare Ray ID found at the bottom of this page.
You can also compare different levels for given factors, such as whether a cultivar from nursery A produces a higher yield, better taste, or both than a plant from nursery B. Strawberries also need plenty of water to ensure juiciness; applying 1ml of water would be difficult to accurately achieve and, possibly, trigger drought stress responses. Sometimes your DOE factors do not behave the same way when you look at them together as opposed to looking at the factor impact individually. In the world of pharmaceuticals, you hear a lot about drug interactions. But taking them both at the same time can cause an interaction effect that can be deadly.
How Design of Experiments enriches life sciences' findings - pharmaphorum
How Design of Experiments enriches life sciences' findings.
Posted: Fri, 20 Jan 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
What is the Scientific Method?
We would have missed out acquiring the optimal temperature and time settings based on our previous OFAT experiments. Say we want to determine the optimal temperature and time settings that will maximize yield through experiments. In a true experiment design, the participants of the group are randomly assigned. So, every unit has an equal chance of getting into the experimental group. In this article, we are going to discuss these different experimental designs for research with examples.
All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies. For all open access content, the Creative Commons licensing terms apply. This comprehensive study guide offers 1,000+ exam-like questions for Green Belts (2,000+ for Black Belts) with full answer walkthroughs, access to instructors, detailed study material, and more. Here we want to define the interactions that will be in the experiment and understand how to analyze those interactions. Numerous quantitative factors (e.g. hours of sunlight, grams of plant food, and liters of water) or qualitative factors (e.g. the cultivar) can influence the strawberry crop (Figure 2).
Experimental research design should be used when a researcher wants to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between variables. It is particularly useful when studying the impact of an intervention or treatment on a particular outcome. Inferential statistics are used to make inferences or generalizations about a larger population based on the data collected in the study. This involves dividing participants into subgroups or blocks based on specific characteristics, such as age or gender, in order to reduce the risk of confounding variables. This involves randomly assigning participants to different groups or treatments to ensure that any observed differences between groups are due to the treatment and not to other factors.
The control group tells us what would have happened to your test subjects without any experimental intervention. First, you may need to decide how widely to vary your independent variable. Start by simply listing the independent and dependent variables. As well as these savings, DOE achieves higher precision and reduced variability when estimating the effects of each factor or interaction than using OFAT. It also systematically estimates the interaction between factors, which is not possible with OFAT experiments. Design of experiments allows you to test numerous factors to determine which make the largest contributions to yield and taste.
Apart from these types of experimental design research in statistics, there are other two methods used in the research process such as randomized block design and completely randomized design. With three variables, machine speed, fill speed, and carbonation level, how many different unique combinations would you have to test to explore all the possibilities? Which combination of machine speed, fill speed, and carbonation level will give you the most consistent fill? The experimentation using all possible factor combinations is called a full factorial design. The study of the design of experiments is an important topic in metascience.
Below is an example of a table that shows the yield that was obtained when changing the volume from 500 to 700 ml. In the scatterplot on the right, we have plotted the measured yield against the change in reaction volume, and it doesn’t take long to see that the best volume is located at 550 ml. So, for example, first we might fix the pH at 3, and change the volume of the reaction container from a low setting of 500ml to a high of 700ml. In order to understand why Design of Experiments is so valuable, it may be helpful to take a look at what DOE helps you achieve. A good way to illustrate this is by looking at an alternative approach, one that we call the “COST” approach. It’s also helpful to see an example of the kinds of Factors that are in an Experiment.
Project Managers who excel in planning will be able to apply that skill to the running of a Design of Experiments for their project. Specific tasks must be conducted in a certain sequence to achieve statistically relevant results. We can see three main reasons that DOE Is a better approach to experiment design than the COST approach. In this way, DOE allows you to construct a carefully prepared set of representative experiments, in which all relevant factors are varied simultaneously. The optimal combination for the best yield would be a volume of 550 ml and pH 4.5.
With the diagram, you see different factors such as the equipment (oven) and ingredients. In your design, you must capture the factors specifically so that, just as in any experiment, you can replicate them. If your cake burns on the bottom, is it the heating process (conventional / convection), is it the powering source (electrical or gas), and/or is it the placement of the racks (bottom, middle, top) within the oven? Or do all three aspects of the oven factor impact the interactions among other factors and your final result? You must accurately document each factor to better know how changes may shape the outcome.

No comments:
Post a Comment